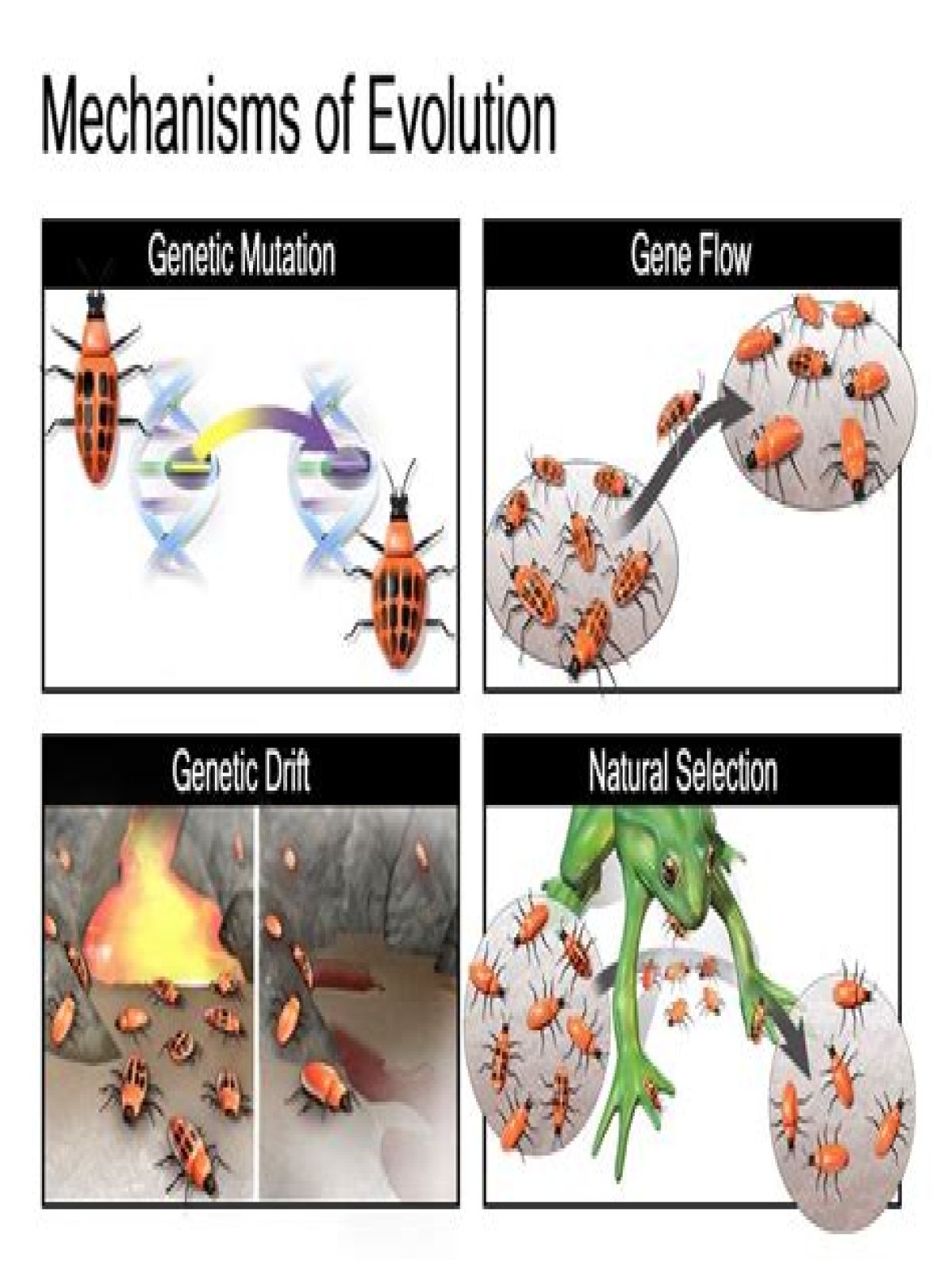
- How Does Gene Flow Lead To Evolution?
- Why is gene flow important to evolution?
- What is an example of gene flow in evolution?
- Does gene flow speed up evolution?
- When is gene flow beneficial?
- How does gene flow affect natural selection?
- How does gene flow directly contribute to evolution gene flow contributes to evolution by?
- How is gene flow accomplished?
- What causes gene flow?
- What happens when gene flow stops between populations?
- How does gene flow affect mutation?
- Can gene flow increase the fitness in a population?
- Which factor does not lead to evolution?
- How can gene flow decrease fitness?
- How do gene flow and genetic drift affect evolution of species?
- How does gene flow affect genetic drift?
- How does gene flow counteract genetic drift?
- Does gene flow increase genetic diversity?
- What produces gene flow quizlet?
- Is gene flow the most important evolutionary force in plants?
- How does migration cause evolution?
- Why is gene flow important to anthropology?
- What’s an example of gene flow?
- When does the process of gene flow take place?
- How does gene flow homogenize populations?
- Does gene flow make populations more similar?
- How does gene flow affect neighboring populations?
- How is a gene pool and biological evolution related?
- How do pollinators contribute to the gene flow?
- When is genetic drift a major factor in evolution?
- Is gene flow based on adaptation?
- What are 5 factors that can lead to evolution?
- What factors lead to the evolution of a species?
- How genetics and evolution influence each other?
- The Evolution of Populations: Natural Selection, Genetic Drift, and Gene Flow
- Biology Basics: Gene Flow (Simplified)
- Gene Flow
- Genetic Drift
- Related Articles
How Does Gene Flow Lead To Evolution?
Evolution can also occur as a result of genes being transferred from one population to another. This gene flow occurs when there is migration. The loss or addition of people can easily change gene pool frequencies even if there are no other evolutionary mechanisms operating.
Why is gene flow important to evolution?
The effect of gene flow is to reduce genetic differences between populations, thereby preventing or delaying the evolution of the populations in different geographical areas into separate species of the pathogen.
What is an example of gene flow in evolution?
Gene flow is the Chiweenie (Chihuahua/Dachshund), shown below. As one dog from a specific population is allowed to breed within a pure-breeding group, new alleles are brought into the mix. The gene pool is expanded, and new varieties are seen. Thus, the labradoodle has a Labrador mentality, but has Poodle hair.
Does gene flow speed up evolution?
Gene flow could facilitate adaptive evolution
Large populations in favorable environments typically have greater growth rates (λ) and produce more emigrants than populations in marginal habitats or those at the edges of the range.
When is gene flow beneficial?
Early on, gene flow was seen largely as a benefit for populations at risk of extinction as an agent that would reverse those hazards (Lacy 1987). The intentional introduction of new genetic diversity for the purposes of sustaining a population is called “genetic rescue” (Tallmon et al. 2004).
How does gene flow affect natural selection?
Gene flow and natural selection are two central, and usually opposing, evolutionary forces: gene flow distributes, homogenizes, and maintains genetic variation that can act as the ‘stuff of evolution’, while natural selection reduces genetic variation to the variants that favor survival and reproduction.
How does gene flow directly contribute to evolution gene flow contributes to evolution by?
The introduction of new alleles through gene flow increases variability within the population and makes possible new combinations of traits. … Although gene flow does not change allele frequencies for a species as a whole, it can alter allele frequencies in local populations.
How is gene flow accomplished?
Gene flow is the exchange of genes between two separate populations. This is most often accomplished when animals or spores from plants migrate to a new area. Any time a gene is introduced into a population where that gene once did not exist, gene flow has occurred.
What causes gene flow?
Gene flow is the movement of genes into or out of a population. Such movement may be due to migration of individual organisms that reproduce in their new populations, or to the movement of gametes (e.g., as a consequence of pollen transfer among plants).
What happens when gene flow stops between populations?
How does gene flow affect mutation?
Can gene flow increase the fitness in a population?
Alternatively, gene flow from central populations may increase effective population size and genetic variation in edge populations, thereby ultimately increasing fitness at the range limit and perhaps contributing to range expansion (4–6).
Which factor does not lead to evolution?
environmental change does NOT cause evolution to occur. a temperature or climate change does not itself force a species to change its inherited characteristics. if this were the case, then all species would be able to adapt to the new environment, and extinction would be a very rare event.
How can gene flow decrease fitness?
Small populations with high genetic load may be constrained in their ability to withstand abrupt environmental stress. Gene flow may ameliorate these genetic constraints by reducing inbreeding depression and introducing adaptive alleles, or could decrease fitness by introducing maladaptive alleles.
How do gene flow and genetic drift affect evolution of species?
Genetic drift can result in the loss of rare alleles, and can decrease the size of the gene pool. Genetic drift can also cause a new population to be genetically distinct from its original population, which has led to the hypothesis that genetic drift plays a role in the evolution of new species.
How does gene flow affect genetic drift?
Genetic drift stems from the chance occurrence that some individuals have more offspring than others and results in changes in allele frequencies that are random in direction. When individuals leave or join the population, allele frequencies can change as a result of gene flow.
How does gene flow counteract genetic drift?
The effects of genetic drift can be overcome by gene flow. If enough individuals are exchanged between two populations that are experiencing independent genetic drift, then the drifting populations become genetically linked and population subdivision will not occur.
Does gene flow increase genetic diversity?
What produces gene flow quizlet?
Population gene pools must become isolated. … What produces gene flow? mating between populations. What is suggested by the hypothesis of punctuated equilibrium?
Is gene flow the most important evolutionary force in plants?
Gene flow in plants is likely to often act as a cohesive force, uniting individual plant species into real evolutionary units. … Most plant evolutionists now recognize the importance of gene flow, and it is receiving increased recognition from other areas of plant biology as well.
How does migration cause evolution?
Migration will generally unify gene frequencies among populations rapidly in evolutionary time. In the absence of selection, migration is a strong force for equalizing the gene frequencies of subpopulations in a species. … Gene flow thus acts to bind the species together.
Why is gene flow important to anthropology?
In anthropology, gene flow more generally refers to allelic change due to movement of individuals from one place to another. … In this way it is the balance of gene flow and genetic drift that dictates a population’s ability to maintain genetic variation.
What’s an example of gene flow?
When does the process of gene flow take place?
During breeding between the members of two different population. Explanation: When a member of a species from one habitat moves to another habitat, then the phenomenon of gene flow may take place.
How does gene flow homogenize populations?
Gene flow between isolated populations slows down their genetic drift from each other and reduces the power of natural selection to promote divergence between them. When there is a great deal of gene flow between populations, they tend to be similar; in this way, gene flow has a homogenizing effect.
Does gene flow make populations more similar?
Gene flow is the movement of genes into or out of a population. … Gene flow tends to reduce the differences between populations because members of each population can interbreed and genes are essentially shared or transferred between the two populations. This makes the two gene pools become more similar.
How does gene flow affect neighboring populations?
Gene flow occurs when individuals join new populations and reproduce. Gene flow keeps neighboring populations similar. Low gene flow increases the chance that two populations will evolve into different species.
Explain how a gene pool and biological evolution are related. Biological evolution is a change in a population’s gene pool over time. A gene pool includes all the genes present in a population. … the next generation would reflect the genes of these few survivors.
How do pollinators contribute to the gene flow?
In cities, pollinator foraging is often sufficient to maintain gene flow between fragmented patches. … Pollinators that move long distances have been documented to maintain population connectivity, limit inbreeding and reduce genetic differences among populations (Ehrlich and Raven, 1969; Lenormand, 2002).
When is genetic drift a major factor in evolution?
The genetic drift is a major factor in evolution when there is lower gene flow and when there is no selective pressure and when there is a bottleneck in the environment.
Is gene flow based on adaptation?
Gene flow is a fundamental evolutionary force in adaptation that is especially important to understand as humans are rapidly changing both the natural environment and natural levels of gene flow.
What are 5 factors that can lead to evolution?
They are: mutation, non-random mating, gene flow, finite population size (genetic drift), and natural selection.
What factors lead to the evolution of a species?
Evolution is a consequence of the interaction of four factors: (1) the potential for a species to increase in number, (2) the genetic variation of individuals in a species due to mutation and sexual reproduction, (3) competition for an environment’s limited supply of the resources that individuals need in order to …
How genetics and evolution influence each other?
Evolution is the process by which populations of organisms change over generations. Genetic variations underlie these changes. … If a trait is advantageous and helps the individual survive and reproduce, the genetic variation is more likely to be passed to the next generation (a process known as natural selection).
The Evolution of Populations: Natural Selection, Genetic Drift, and Gene Flow
Biology Basics: Gene Flow (Simplified)
Gene Flow
Genetic Drift
Related Searches
does gene flow increase genetic variationgene flow pdfgene flow vs genetic driftgene flow examplegene flow example in humansgene flow evolution examplesdoes natural selection increase genetic variation