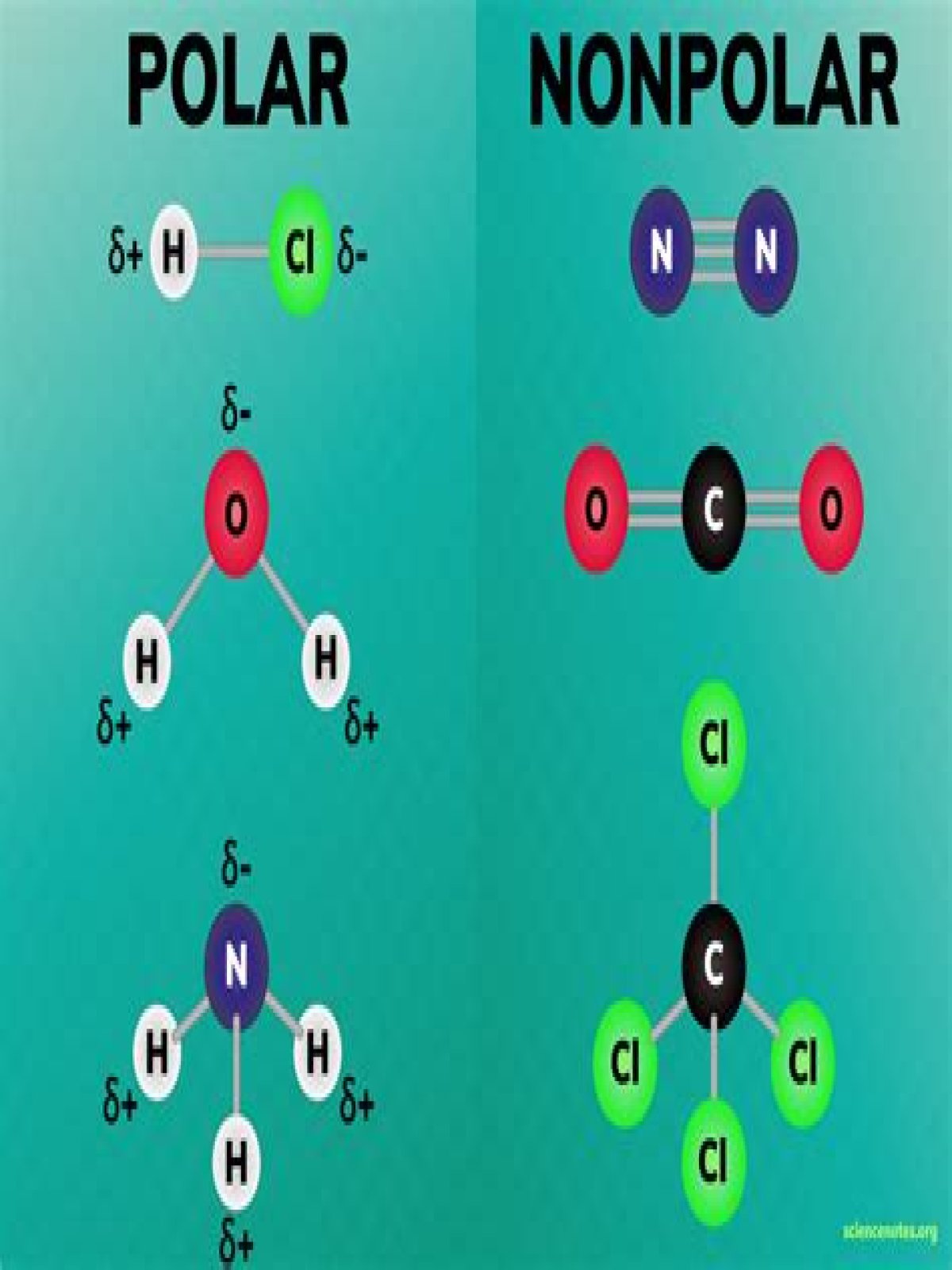
Also question is, what is polar and nonpolar?
Polar molecules occur when there is an electronegativity difference between the bonded atoms. Nonpolar molecules occur when electrons are shared equal between atoms of a diatomic molecule or when polar bonds in a larger molecule cancel each other out.
One may also ask, what is the best definition of polar covalent bond? Polar covalent bond is a chemical bond in which the electrons required to form a bond is unequally shared between two atoms. The atom which is more electronegative attracts more electrons from the bonded pair than the other atom. The bonds formed between two atoms have a permanent electric dipole.
In this way, what is a polar molecule simple definition?
A polar molecule is a molecule containing polar bonds where the sum of all the bond's dipole moments is not zero. Polar bonds form when there is a difference between the electronegativity values of the atoms participating in a bond.
How can you tell if a bond is polar or nonpolar?
Step 2: Identify each bond as either polar or nonpolar. (If the difference in electronegativity for the atoms in a bond is greater than 0.4, we consider the bond polar. If the difference in electronegativity is less than 0.4, the bond is essentially nonpolar.) If there are no polar bonds, the molecule is nonpolar.