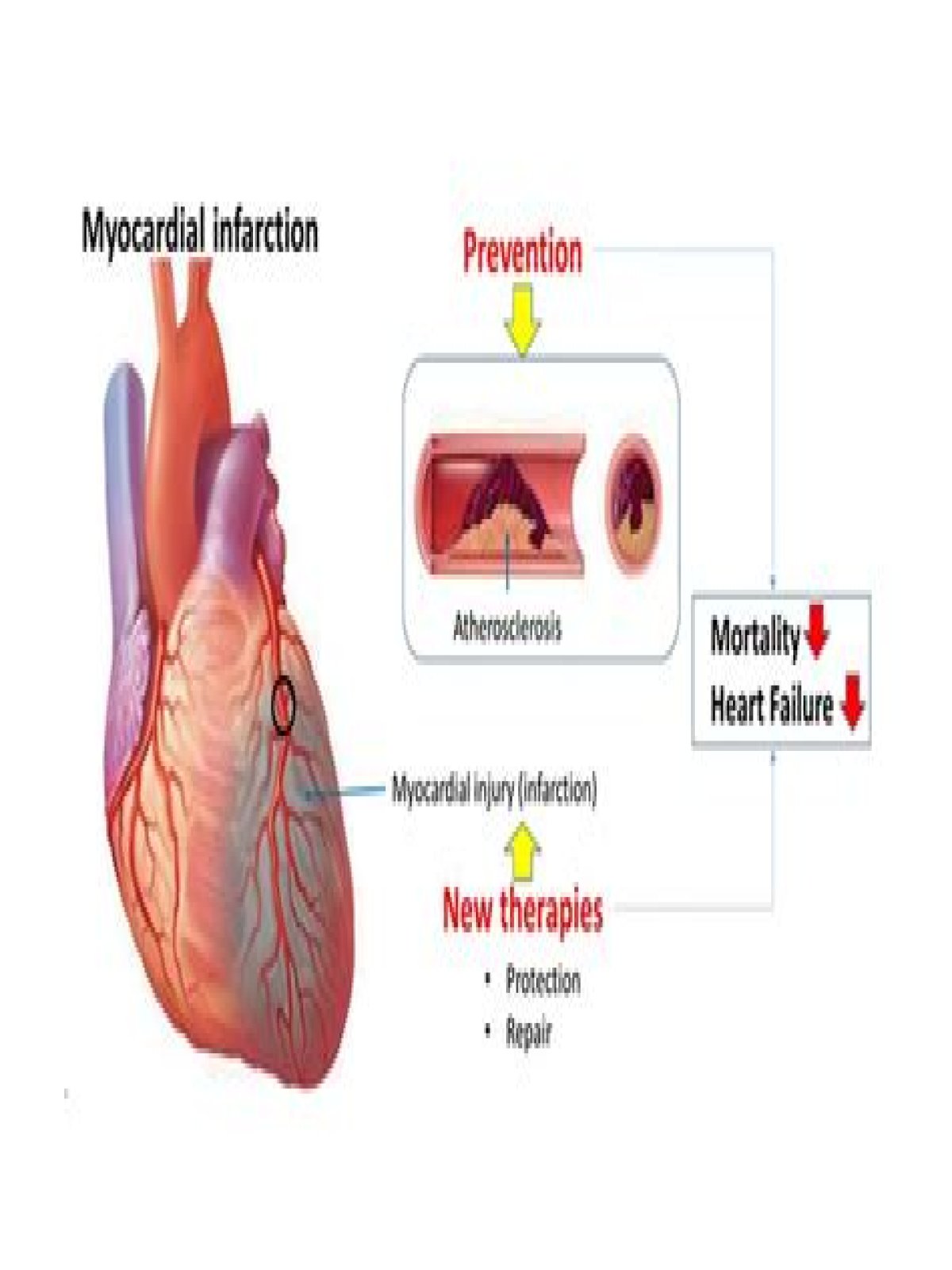
Hereof, what does the word infarct mean in medical terms?
Medical Definition of infarct : an area of necrosis in a tissue or organ resulting from obstruction of the local circulation by a thrombus or embolus.
Also, can infarction be cured? Treatment. If cerebral infarction is caused by a thrombus occluding blood flow to an artery supplying the brain, definitive therapy is aimed at removing the blockage by breaking the clot down (thrombolysis), or by removing it mechanically (thrombectomy).
In respect to this, is infarct a stroke?
Infarction or Ischaemic stroke are both names for a stroke caused by a blockage in a blood vessel in the brain. This is the most common type of stroke. Alternatively a blood clot or fatty plaque formed elsewhere in the body breaks off which then travels to the brain where it blocks a blood vessel (Embolus).
What is the difference between ischemia and infarction?
Both terms, ischemia and infarction, are used here. Ischemia denotes diminished volume of perfusion, while infarction is the cellular response to lack of perfusion. Some of the changes discussed here are the result of ischemia such as those involving myocardial substrate extraction.
What is the difference between necrosis and infarction?
What is an infarction in legal terms?
What is another word for myocardial infarction?
What is the difference between stroke and myocardial infarction?
What do you mean by necrosis?
How does a stroke happen?
What is meant by old infarct?
What is the meaning of ischemic?
What causes an infarct?
What is the treatment for brain infarction?
Can stress cause a stroke?
Is a brain infarct a stroke?
Can cerebral infarction cause death?
Can stroke damage be reversed?
What is chronic stroke?
What are the 2 types of strokes?
- Ischemic Stroke (Clots) Occurs when a blood vessel supplying blood to the brain is obstructed.
- Hemorrhagic Stroke (Bleeds) Occurs when a weakened blood vessel ruptures.
- TIA (Transient Ischemic Attack) Called a “mini stroke,” it's caused by a serious temporary clot.
- Cryptogenic Stroke.