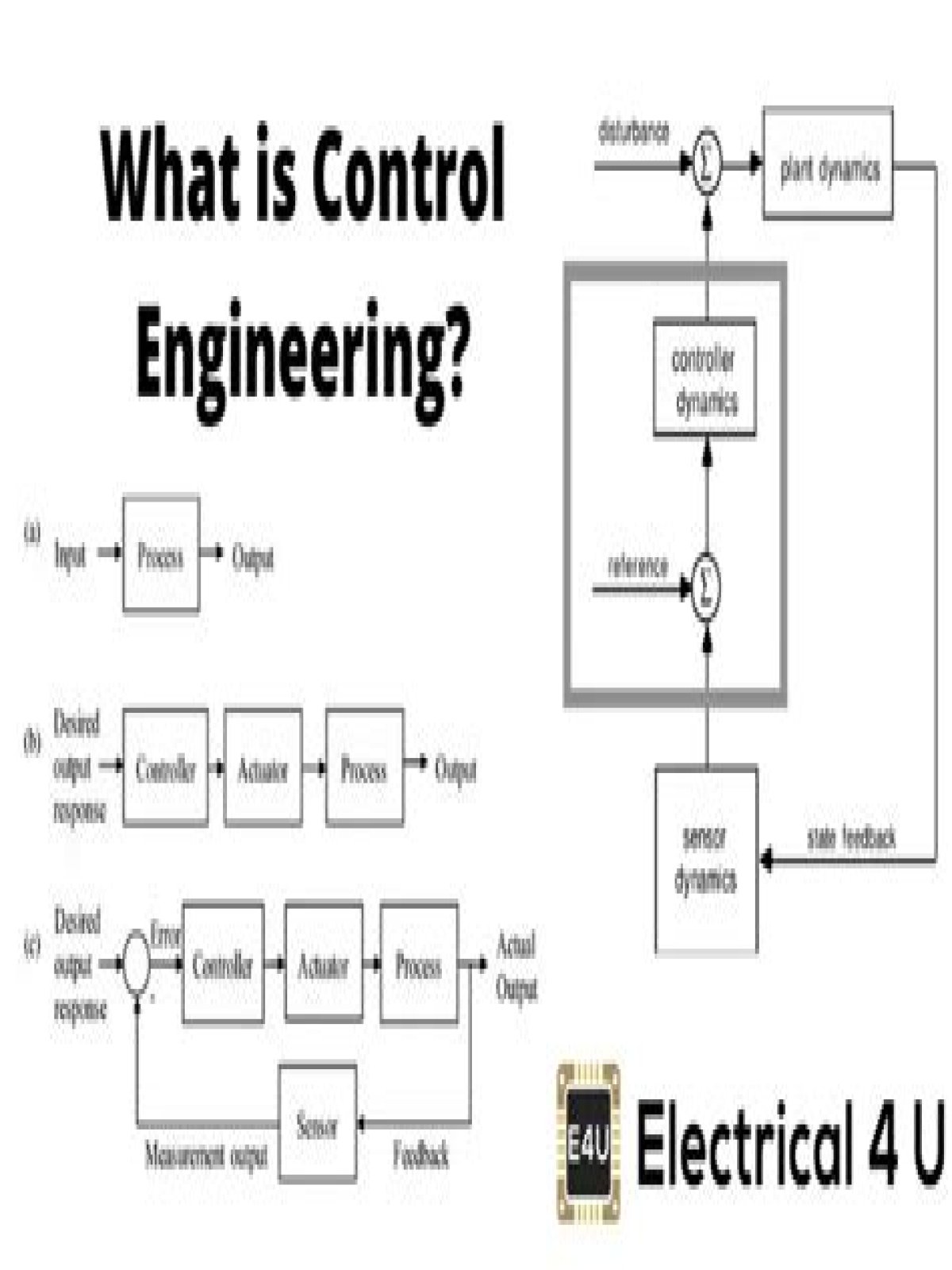
Similarly, it is asked, what is an example of an engineering control?
Engineering controls protect workers by removing hazardous conditions or by placing a barrier between the worker and the hazard. Examples include local exhaust ventilation to capture and remove airborne emissions or machine guards to shield the worker.
Likewise, what are the three engineering controls? Traditionally, a hierarchy of controls has been used as a means of determining how to implement feasible and effective controls, which typically include elimination, substitution, engineering controls, administrative controls, and personal protective equipment.
People also ask, what does engineering control mean?
Definition. Engineering controls eliminate or reduce exposure to a chemical or physical hazard through the use or substitution of engineered machinery or equipment.
What are engineering controls in healthcare?
The revised definition of engineering controls means “controls (e.g. sharps, disposal containers, self sheathing needles, safer medical devices such as sharps with engineered injury protections and needleless systems) that isolate or remove the bloodborne pathogens hazard from the work place”.
What are the 5 major categories of control measures?
- Elimination;
- Substitution;
- Engineering controls;
- Signage/warnings and/or administrative controls;
- Personal protective equipment.
What is engineering control in OSHA?
Are gloves an engineering control?
What are the 3 levels of hazard control?
- Elimination.
- Substitution.
- Engineering controls.
- Administrative controls.
- Personal protective equipment.
What is the difference between engineering controls and work practice controls?
When should PPE be used?
What is administrative control in safety?
What are the steps in the hierarchy of control?
- Elimination – removes the cause of danger completely.
- Substitution – controls the hazard by replacing it with a less risky way to achieve the same outcome.
- Isolation – separates the hazard from the people at risk by isolating it.
What is an example of an engineering control for silica?
Is Loto an engineering control?
What are the four main ways hazards are typically controlled?
Engineering Controls include;
- elimination.
- isolation.
- substitution.
- automation.
- machine guarding & re-design.
- local exhaust ventilation; and.
- air make-up systems.
What are examples of work practice controls?
What are administrative controls OSHA?
How can physical hazards be controlled?
- Providing safety equipment to employees that reduces their exposure to the physical safety hazard.
- Reduce noises and vibrations present in the workplace.
- Place barriers between employees and physical hazards such as radiation or microwaves.
How do you control hazards?
- Eliminate the hazard.
- Substitute the hazard with a lesser risk.
- Isolate the hazard.
- Use engineering controls.
- Use administrative controls.
- Use personal protective equipment.