Also to know is, what is a K strategist?
K-selected species, also called K-strategist, species whose populations fluctuate at or near the carrying capacity (K) of the environment in which they reside.
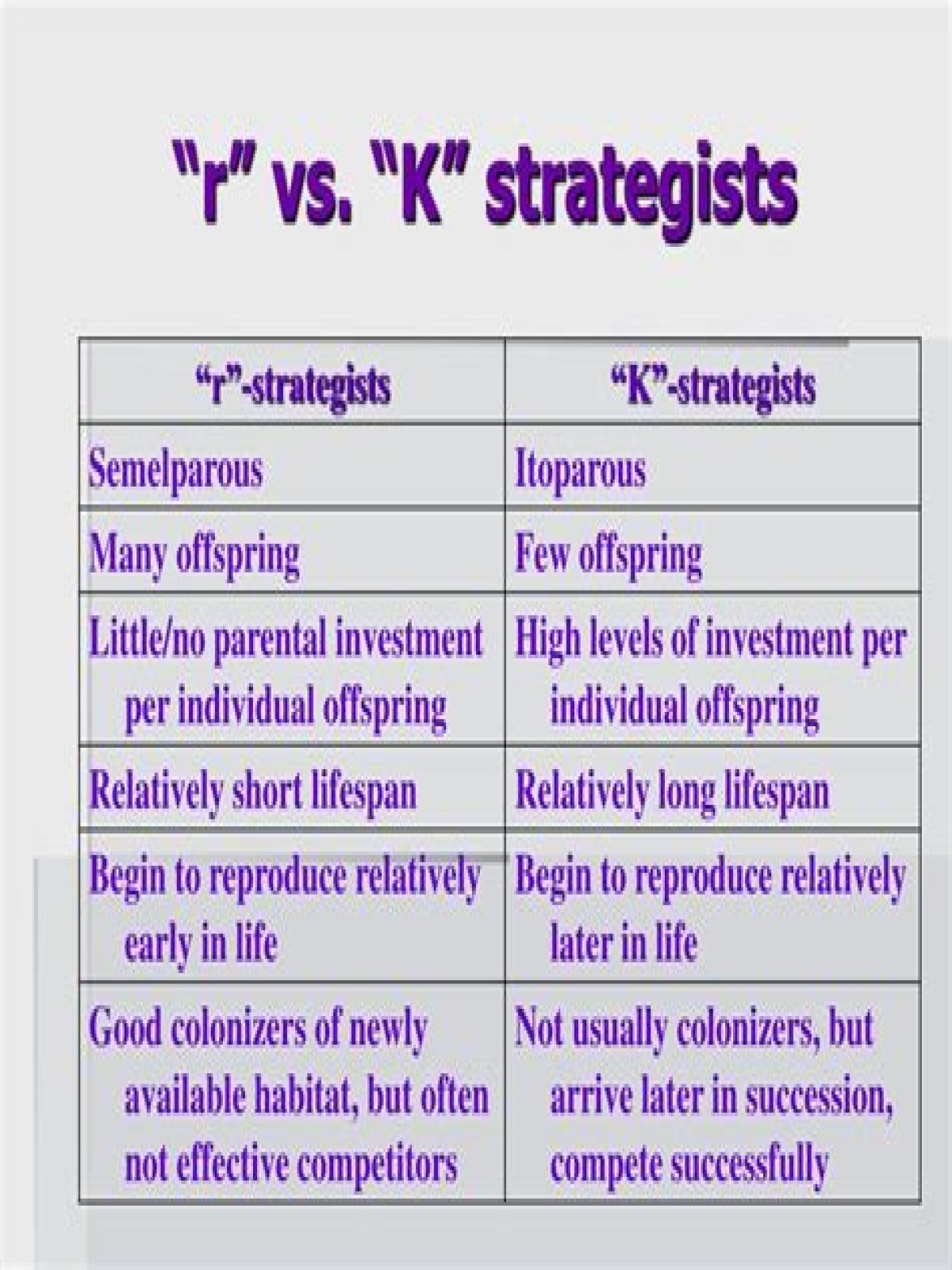
Beside above, what is an R strategist and K strategist? The two evolutionary "strategies" are termed r-selection, for those species that produce many "cheap" offspring and live in unstable environments and K-selection for those species that produce few "expensive" offspring and live in stable environments.
Consequently, what is the difference between a K and R strategist species?
The r selected species live in populations that are highly variable. The fittest individuals in these environments have many offspring and reproduce early. K selected species live in populations that are at or near equilibrium conditions for long periods of time.
What are characteristics of R strategists?
Among the traits that are thought to characterize r-selection are high fecundity, small body size, early maturity onset, short generation time, and the ability to disperse offspring widely. Organisms whose life history is subject to r-selection are often referred to as r-strategists or r-selected.