Likewise, what is a mixed Anova used for?
In statistics, a mixed-design analysis of variance model, also known as a split-plot ANOVA, is used to test for differences between two or more independent groups whilst subjecting participants to repeated measures.
Secondly, how many independent variables can a mixed model Anova compare at one time? A mixed model ANOVA is a combination of a between-unit ANOVA and a within-unit ANOVA. It requires a minimum of two categorical independent variables, sometimes called factors, and at least one of these variables has to vary between-units and at least one of them has to vary within-units.
Beside above, what is a 2x2 mixed Anova?
Two-factor mixed-design ANOVA -> A mix of 1 between-subjects and 1 within-subjects factor. -> a DV measurement is repeatedly conducted for each level of the. within-subjects factor with(in) the same subject. -> For the other between-subjects factor you must use. a different group of subjects for each factor level.
What is the full meaning of Anova?
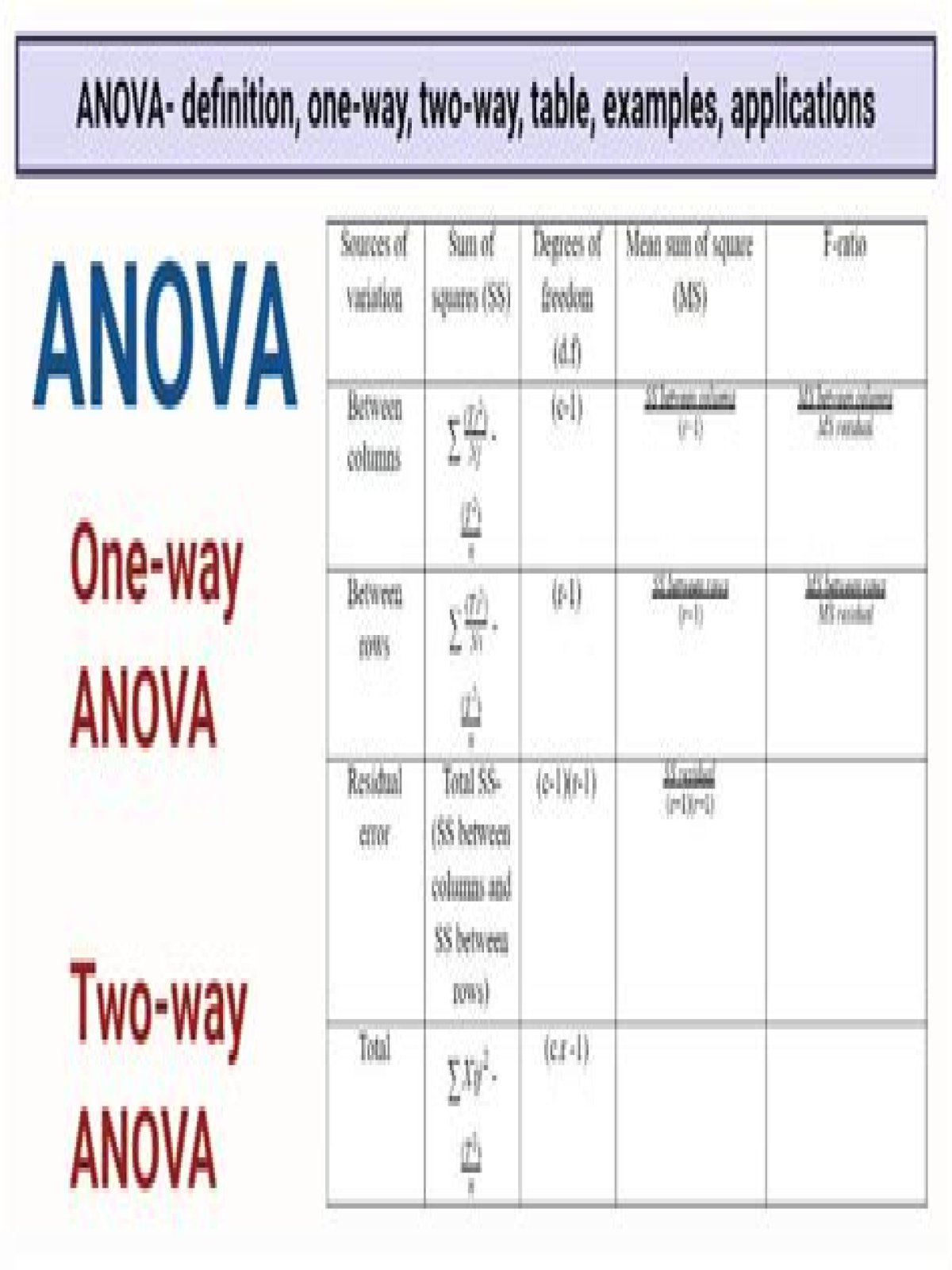
ANOVA Defined The acronym ANOVA refers to analysis of variance and is a statistical procedure used to test the degree to which two or more groups vary or differ in an experiment. In most experiments, a great deal of variance (or difference) usually indicates that there was a significant finding from the research.
What are the different types of Anova?
What does 2x3 Anova mean?
What is a mixed factorial design?
What does Ancova tell?
What is a mixed design study?
What is difference between one way Anova and two way Anova?
What is a between subjects Anova?
When would you use a repeated measures Anova?
How many hypotheses are there in a 2x2 factorial design?
Can an experiment be both within and between subjects?
How do you interpret a repeated measures Anova in SPSS?
- Click Analyze -> General Linear Model -> Repeated Measures.
- Name your Within-Subject factor, specify the number of levels, then click Add.
- Hit Define, and then drag and drop (left to right) a variable for each of the levels you specified (taking care to preserve their correct order)