Also to know is, how is break even point calculated?
To calculate a break-even point based on units: Divide fixed costs by the revenue per unit minus the variable cost per unit. When determining a break-even point based on sales dollars: Divide the fixed costs by the contribution margin.
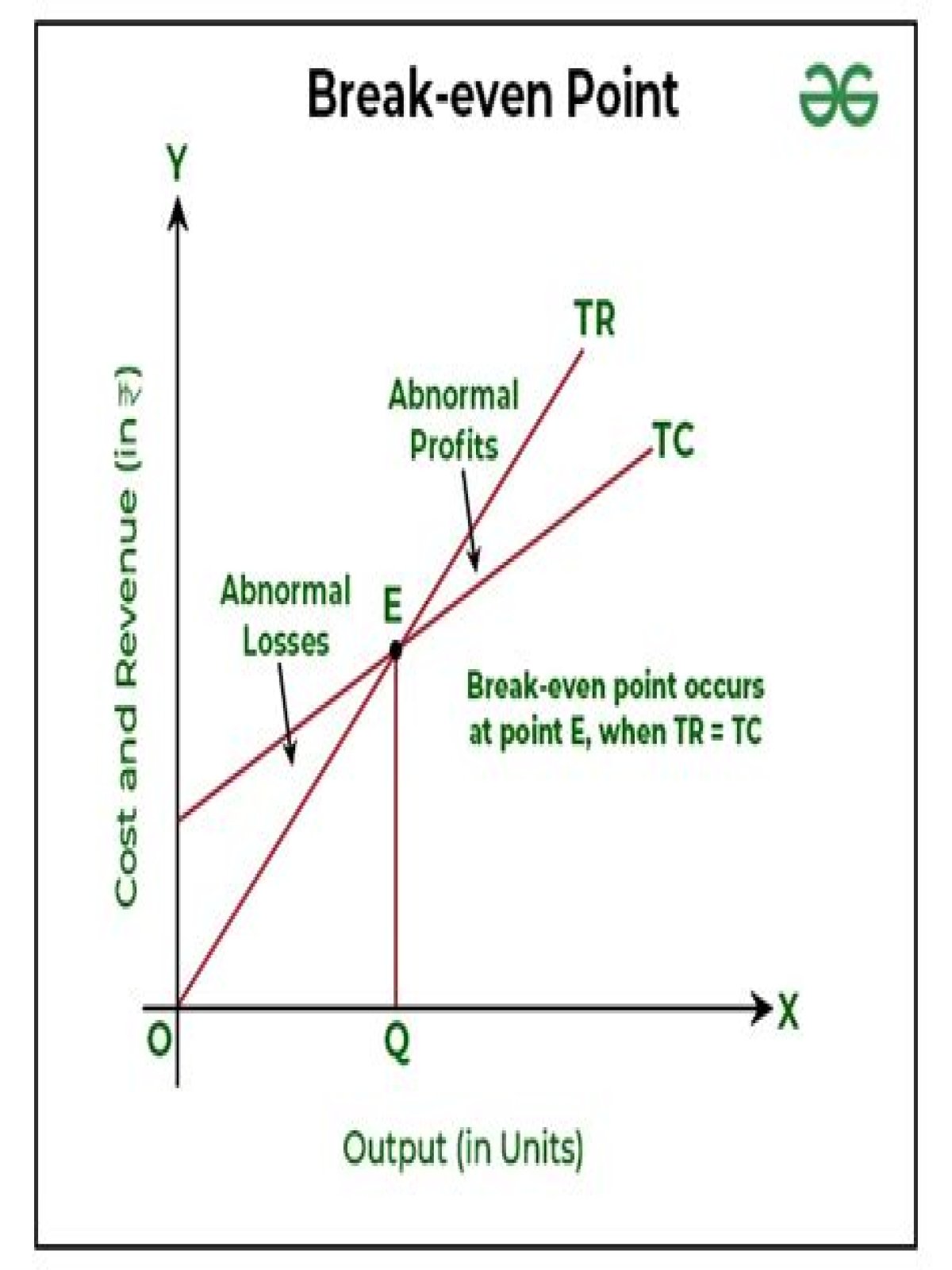
One may also ask, what is the break even point quizlet? The break-even point is the point where total revenue equals total cost (i.e., the point of zero profit). New companies typically experience losses (negative operating income) initially and view their first break-even period as a significant milestone.
People also ask, what is the meaning of break even point?
Definition: The break even point is the production level where total revenues equals total expenses. In other words, the break-even point is where a company produces the same amount of revenues as expenses either during a manufacturing process or an accounting period.
Why is break even important?
Break-even analysis is an important aspect of a good business plan, since it helps the business determine the cost structures, and the number of units that need to be sold in order to cover the cost or make a profit.