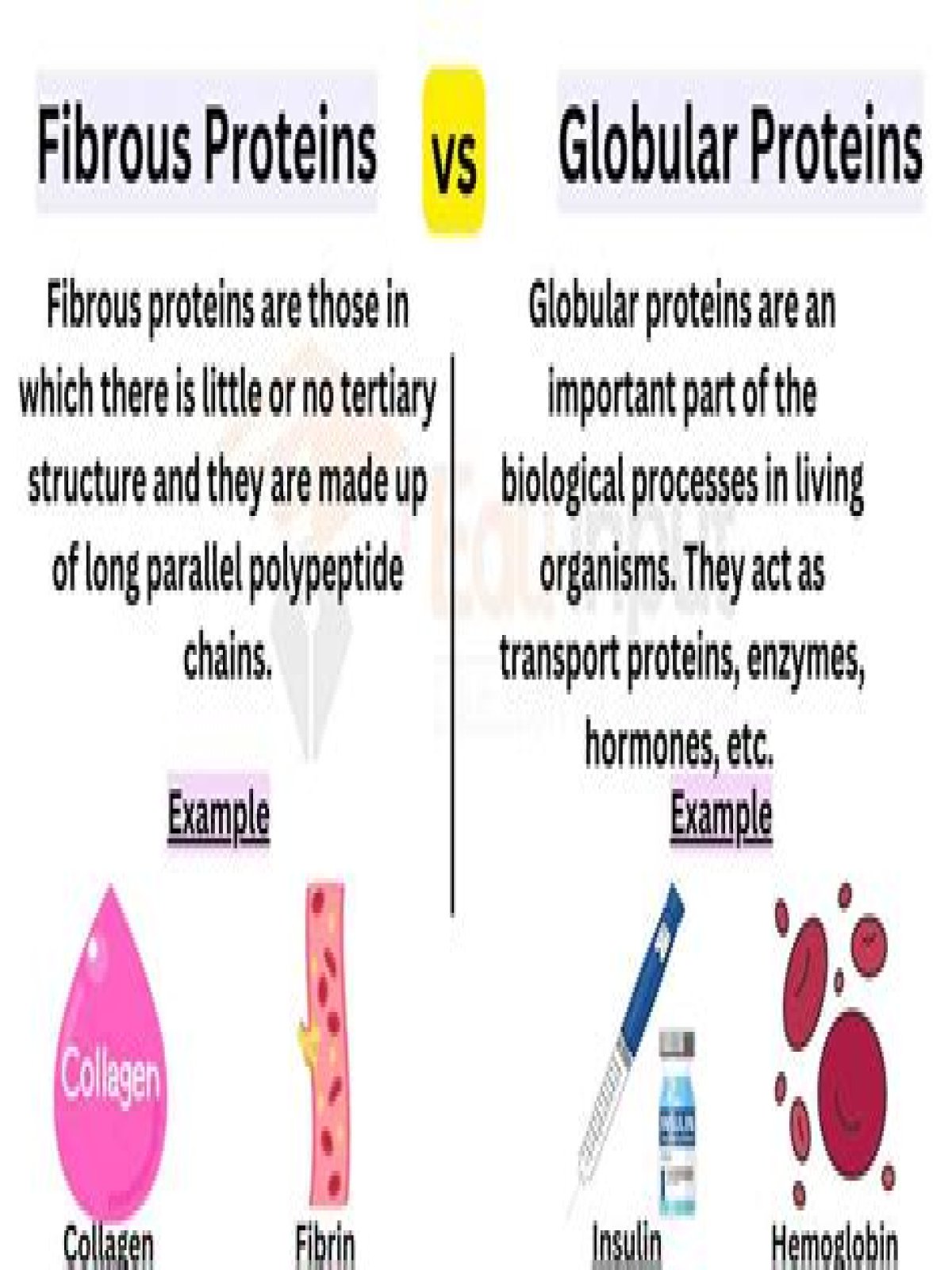
Thereof, why are fibrous proteins strong?
The amino acid sequences of fibrous proteins often contain repeating sets of amino acid residues . Such repeating sets tend to cause the protein to be both elongated and strong. Fibrous proteins also gain strength due to interactions between the side chains of the residues.
Furthermore, why are globular proteins important? Globular proteins play many biological roles, including acting as enzymes, hormones, immunoglobulins, and transport molecules. Hemoglobin is a globular protein found in red blood cells. It is made of four polypeptide chains, each containing a heme group that binds and transports oxygen through the blood stream.
Additionally, where are fibrous proteins found?
Collagen is an abundant fibrous protein in vertebrate animals being found in tendons, cartilage and bone, and it has a unique structure. Elastin is an important component of tissues, such as ligaments and skin, and is highly elastic.
How are fibrous proteins formed?
When a protein loses its shape in this way it is said to be Denatured. Fibrous - They proteins form long fibres and mostly consist of repeated sequences of amino acids which are insoluble in water. They usually have structural roles, such as: Collagen in bone and cartilage, Keratin in fingernails and hair.
What foods contain fibrous proteins?
Here are examples of foods high in protein with the number of grams per 100 grams of the food:
- Soya beans - 35.9g.
- Cheese - 30.9g.
- Venison - 30.21.
- Pumpkin seeds - 28.8g.
- Lobster - 26.41.
- Canned tuna fish - 26.3g.
- Tuna fish - 25.6g.
- Monkfish - 24g.