Beside this, why do companies use fringe benefits?
Fringe benefits serve as additional compensation. Providing unique fringe benefits to employees helps the company stand out from its competitors. It provides a greater opportunity to attract high value and talented employees from schools or from competing companies.
Additionally, what is fringe benefits advantages and disadvantages? However, there are also a variety of disadvantages of offering fringe benefits. For example, they represent a certain expense to the employer, a particularly high expense for small employers. For certain benefits, it is difficult for employers to offer them without substantial expense such as healthcare.
Considering this, is an example of a fringe benefit provided by a company to its employees?
Fringe benefits are forms of compensation you provide to employees outside of a stated wage or salary. Common examples of fringe benefits include medical and dental insurance, use of a company car, housing allowance, educational assistance, vacation pay, sick pay, meals and employee discounts.
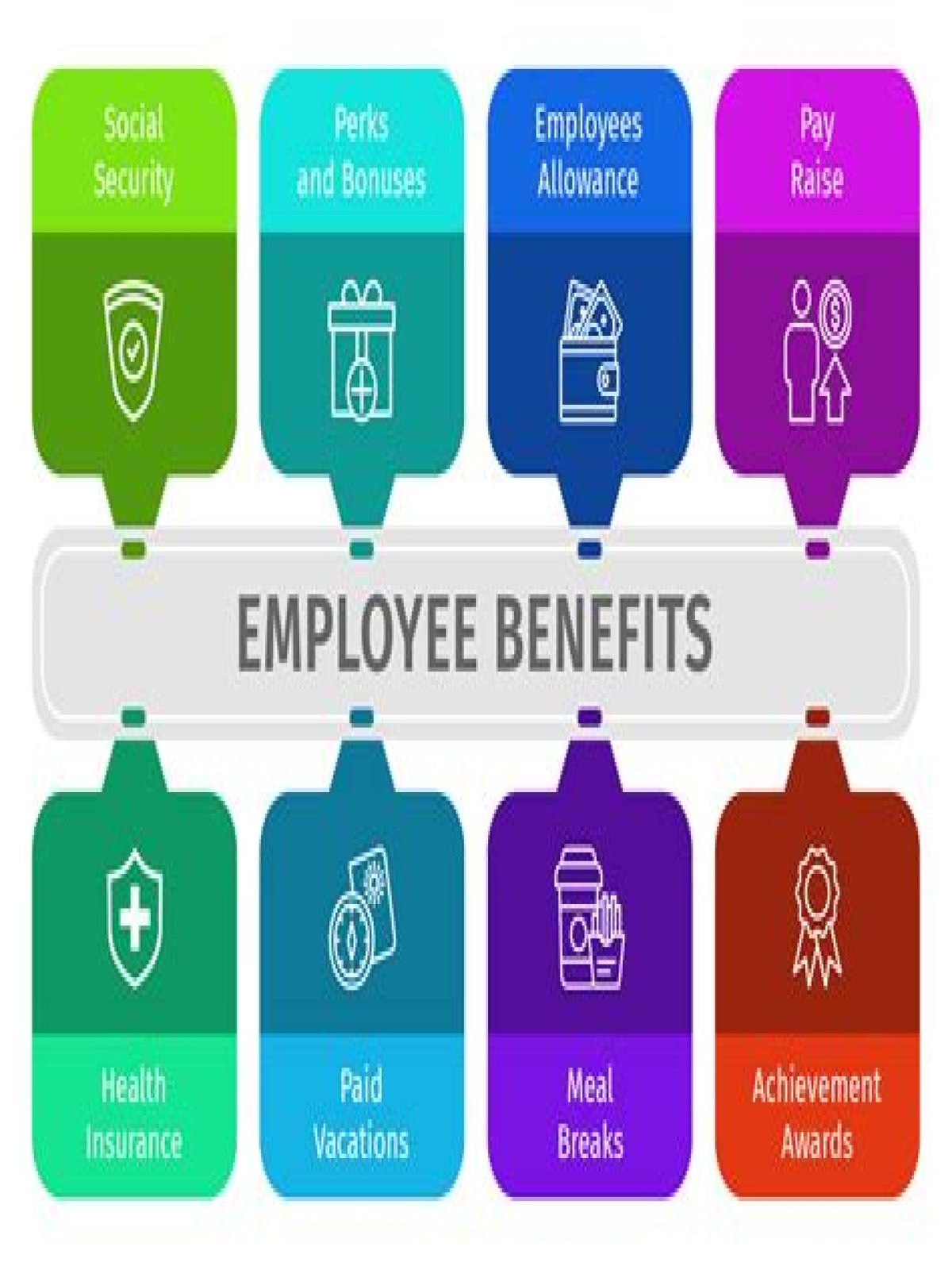
What are the types of fringe benefits?
Types of Fringe Benefits – 8 Major Types: Employee Welfare, Social Security, Employee Security, Payments for Time Not Worked, Health Benefits and a Few Others
- Employee Welfare:
- Social Security:
- Employee Security:
- Payments for Time Not Worked:
- Health Benefits:
- Retirement Benefits:
- Compensation Benefits:
Are fringe benefits worth it?
Fringe benefits = happy employees, but get the tax right!
| Total annual kilometres travelled | % |
|---|---|
| 15,000 to 24,999 | 20 |
| 25,000 to 40,000 | 11 |
| More than 40,000 | 7 |
What are the objectives of fringe benefits?
What is a typical fringe rate?
How is fringe benefit calculated for a company car?
What does reportable fringe benefits mean?
What is a company car worth in salary?
Are fringe benefits taken out of salary?
What fringe benefits are required by law?
What attracts FBT?
What are examples of taxable fringe benefits?
- Bonuses.
- The value of the personal use of an employer-provided vehicle.
- Group-term life insurance in excess of $50,000.
- Vacation expenses.
- Frequent-flyer miles earned during business use, converted to cash.
- Amounts paid to employees for relocation in excess of actual expenses.