People also ask, what is Sctp used for?
Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) is a transport-layer protocol that can be used on top of IP networks for end-to-end communications. SCTP is an IETF standard developed by the Transport Area Working Group (tsvwg).
Additionally, what is s1 in LTE? The S1 user plane external interface (S1-U) is defined between the LTE eNodeB and the LTE S-GW. The S1-U interface provides non guaranteed data delivery of LTE user plane Protocol Data Units (PDUs) between the eNodeB and the S-GW.
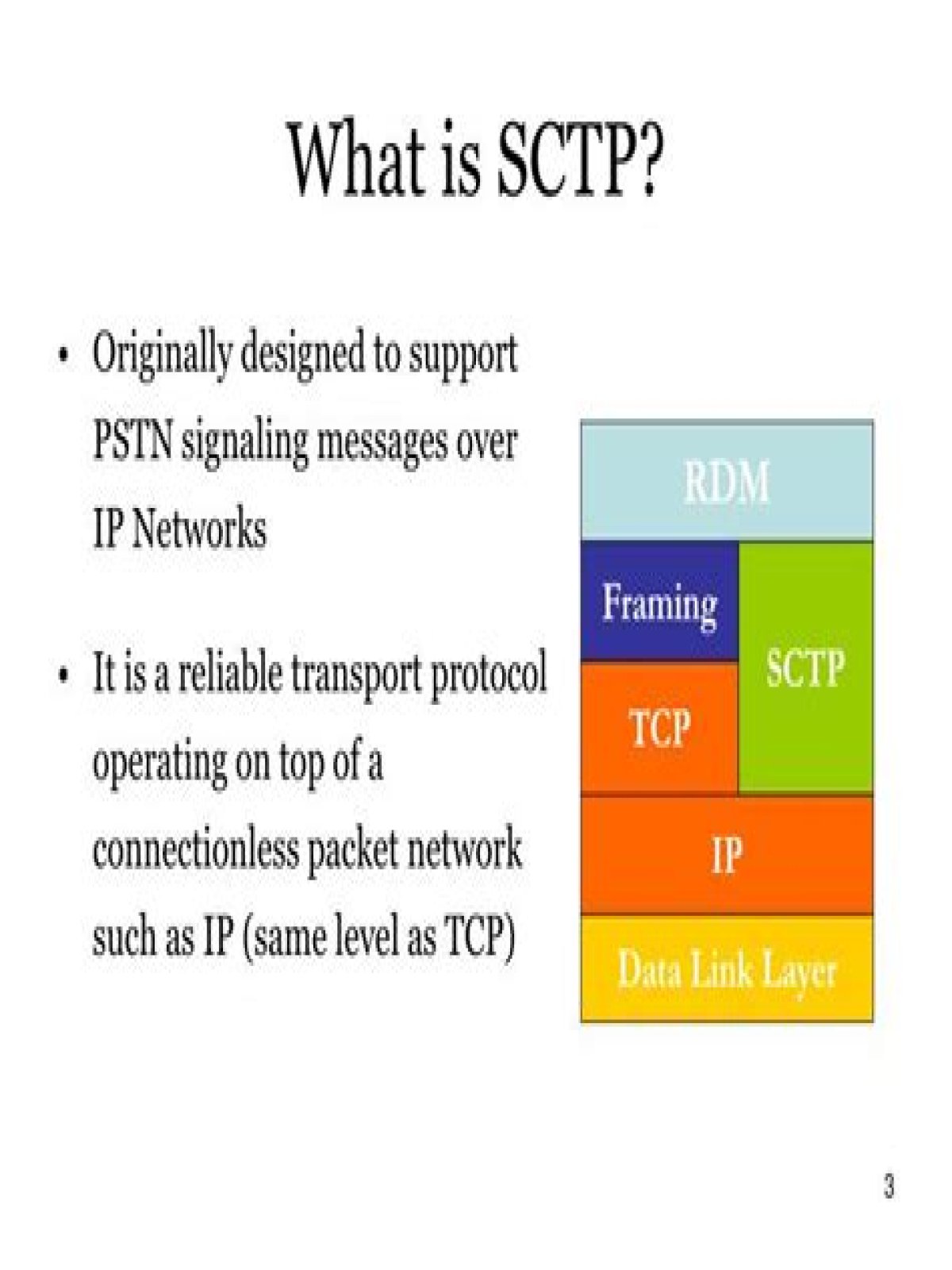
Also know, what is SCTP?
SCTP (Stream Control Transmission Protocol) is a protocol for transmitting multiple streams of data at the same time between two end points that have established a connection in a network. SCTP is a standard protocol (RFC 2960) developed by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF).
What is SCTP port number?
The assigned protocol number for SCTP on IP is 132.